Lavender (Lavandula angustifolia L.)
The natural range of lavender is mainly the Canary Islands, North and East Africa, Australia, Southern Europe, the Arabian Peninsula and India. Lavender flowers are used in aromatherapy because they have a calming effect on the central nervous system as well as the respiratory nervous system. Also, lavender is very widely used for medicinal purposes, for example, taking capsules containing lavender oil orally promotes daily calmness, resistance to stress, falling asleep and good sleep.
Lavender is a perennial plant of the Labiatae family with thousands of years of history. It is a small, fragrant shrub that reaches a maximum height of 80 centimetres and is both a nectar plant and an essential oil plant. Lavender has oppositely arranged, grey-green, lanceolate leaves with a curled edge. The flowers are double-lipped, blue or violet-blue, arranged in false spikes, which in turn form a spike at the end of the inflorescence.
The lavender genus includes up to 47 species. Under natural conditions, lavender grows in North and East Africa, Australia, the Arabian Peninsula, India, the Canary Islands and Southern Europe. However, as a crop it is found all over the world.
Looking at the great variety of species, three main types can be distinguished: English, Spanish and French lavender. Although they share many similarities, French and English varieties can be distinguished by appearance, growth habit, flowering time, fragrance and use.
English or “true” lavender (Lavandula officinalis angustifolia) is more dense, with a fuller flower, and it is this lavender species that is mostly used for medicinal purposes.
Its flowers contain 3% essential substances, anthocyanins, phytosterols, sugars, minerals and tannins. The qualitative and quantitative composition of lavender essential oil is variable and depends on the genotype, place of growth, climatic conditions, propagation and morphological features. Lavender essential oil contains more than 300 different chemical compositions, the main of which is linalool (the amount varies from 9.3% to 68.8% and has the following medicinal properties: anti-inflammatory, anticonvulsant, relaxant, analgesic, sedative, antidepressant, anti-stress agent and anxiolytic agent), linalyl acetate (amount varies from 1.2% to 59.4%), lavandulyl acetate, ocimene, cineole and terpinen-4-ol.
Lavender essential oil has good antioxidant and antimicrobial activities when applied to the skin, as well as significant positive effects on the digestive and nervous systems when taken orally.
Linalool and linalyl acetate are thought to be the main components of lavender oil, which could be related to sleep-promoting effects by modulating the effects of glutamate and GABA.
Lavender has been shown to act as an anxiolytic aid (anxiety reliever) and as a sedative aid to increase body relaxation and resting, thereby promoting sleep.
Lavender interacts with the neurotransmitter GABA (a chemical naturally produced in the nervous system that allows nerve cells to communicate with each other and a lack or excess of which can cause a variety of mood disorders) to help calm the brain and nervous system, reducing agitation, anger, aggression and anxiety. Lavender also works as a pain reliever.
The toxicity of lavender oil is not a concern. Components such as linalool and linalyl acetate are not mutagenic.
Be careful when using sedative medications (central nervous system depressants) with lavender because they interact.
Lavender can cause drowsiness and slow breathing. Sedatives (medications) can also cause drowsiness and decelerated breathing. Taking lavender with sedative medications can cause breathing problems and/or excessive drowsiness.
Insomnia is one of the most common sleep disorders among the population. This disorder is also among the most frequent complaints in primary health care centres. Lavender is called a “brain broom” in various Eastern traditional medicines, because it is able to “clean” the head in the same way that a broom sweeps a room of debris. It is one of the most commonly used herbs for patients with sleep disorders.
According to the European Medicines Agency assessment report
EMA/HMPC/143183/2010, lavender oil acts as a sedative aid and promotes sleep. Separate studies have shown that individuals reported greater alertness and vigour the morning after exposure to lavender, as well as an increase in non-REM, or slow, light sleep, and a decrease in rapid eye movement (REM) sleep, and its duration.
At the same time, the time before waking up after first falling asleep (waking up after the beginning of sleep) increased.
Plants and herbal medicines for the treatment of various sleep disorders have been used for medicinal purposes for centuries - including lavender. Various, complex biochemical processes in the brain provide us with sleep, incl. interaction with GABAergic signals.
As the main inhibitory neurotransmitter, GABA helps maintain the overall balance of neuronal excitation and inhibition in the central nervous system and plays one of the key roles in brain development and function. More than 20% of all neurons in the brain are thought to be GABAergic. Three different GABA receptors: GABAA, GABAB and GABAC are involved in the regulation of sleep and arousal (although to varying degrees). The most commonly used sleeping pills act directly on the GABA systems, especially benzodiazepine.
Lavender's active ingredients can bind glutamate N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors (NMDA) and serotonin transporters. The NMDA receptor is believed to be crucial for the control of synaptic plasticity and to mediate memory function. Sleep-promoting GABAergic neurons are a major target for the pharmacological treatment of insomnia.
It must be said that despite the availability of several sleep medications, side effects are still a problem and there is still a demand for safer insomnia treatment options. Studies show that several substances of plant origin, incl. found in lavender, can act as sleep inducers by modulating GABAergic signalling in the brain. The safety and wide acceptance (absence of side effects) of herbal products among patients is a strong argument for preferring herbs over industrially produced drugs.

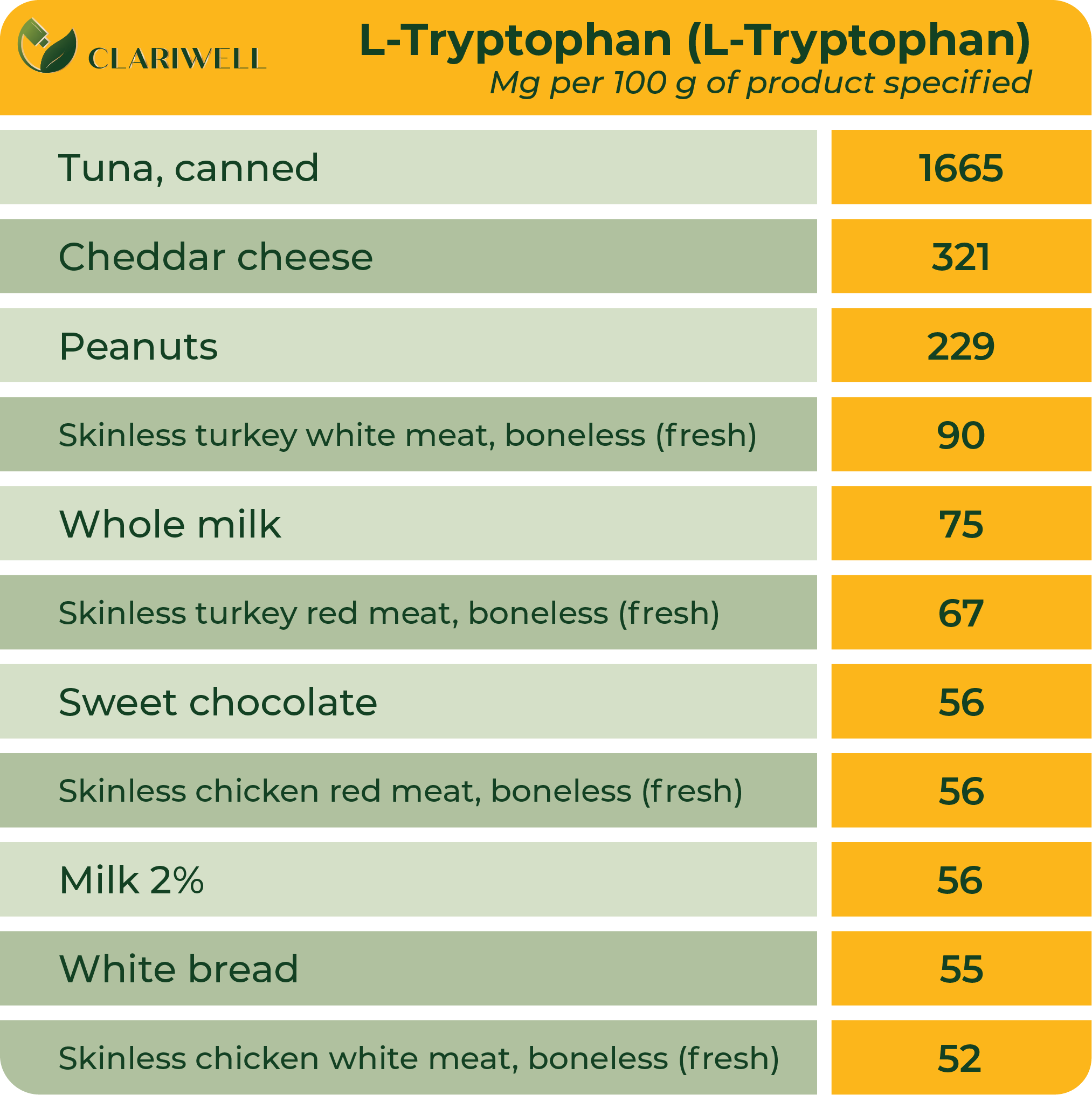
L-Tryptophan (L-Tryptophan)
L-tryptophan is an essential amino acid, a component of natural proteins. Plants and microorganisms can synthesise tryptophan from indole and serine. L-tryptophan is important for many organs in the body. L-tryptophan is not produced by the body, so attention must be paid to its intake. After L-tryptophan is absorbed from food, the body converts some of it into 5-HTP (a metabolic intermediate in the biosynthesis of the neurotransmitter serotonin) and then into serotonin.
Hopkins and Cole discovered tryptophan at the beginning of the twentieth century after isolating it from the casein protein, while Ellinger and Flamand determined its molecular structure shortly thereafter. L-tryptophan (i.e., tryptophan) is one of the eight essential amino acids (amino acids that cannot be synthesised by the human body and must be obtained from the diet).
So L-tryptophan is a unique protein amino acid that has an indole ring. Indole is a typical nitrogen heterocyclic aromatic compound, widely distributed in our daily products and natural environment. The indole ring is present in many alkaloids, phytohormones, plant flower oils, pigments and proteins. Because the indole nucleus has a wide spectrum of biological activities, it is widely used in the pharmaceutical industry.
After L-tryptophan enters various tissues and cells of the body, it is included in protein metabolism and synthesis, and it can also participate in various metabolic processes depending on the expression of specific enzyme activities in the tissues.
L-tryptophan is the only precursor of peripherally and centrally produced serotonin. Serotonin regulates the balance of the nervous system, mental stability, mood and also sleep. On the other hand, melatonin is synthesised from serotonin. As the “output material” of melatonin, serotonin helps regulate sleep cycles and the internal clock. It has been proven that melatonin plays a decisive role in the quality of sleep. Melatonin is a biologically active substance that is formed in our brain during the night (darkness) and regulates the biorhythms of our body - the cycle of sleep and wakefulness. Both melatonin and serotonin are formed from the essential amino acid L-tryptophan, which we can only take in through food or food supplements. Significant amounts of L-tryptophan can be found in various types of cheese and meat.
Food supplements containing L-tryptophan are safe as long as they are not taken on a long-term basis. L-Tryptophan can cause someside effects such as drowsiness, stomach pain, vomiting, diarrhoea, headache, blurred vision, dizziness, palpitations and more.
L-tryptophan can interfere with the effects of many different drugs. Do not take L-tryptophan if you are taking antidepressants known as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), MAO inhibitors, tricyclic antidepressants, and atypical antidepressants. This can lead to a life-threatening condition called serotonin syndrome. Symptoms of serotonin syndrome include:
- • Extreme anxiety
- • Heart palpitations
- • Delirium
- • Severe muscle spasms
- • Increased body temperature
L-tryptophan supplements are not recommended for pregnant women.
Consult your doctor before taking L-tryptophan if you have cirrhosis of the liver.
Always tell your doctor about any food supplements you take, including natural and over-the-counter supplements. In this way, your doctor can check for possible side effects or interactions with any medications.
The main role of L-tryptophan in the human body is a part of protein synthesis. Because tryptophan is found in the lowest concentration of all the amino acids in the body, it is relatively lessavailable and it is considered to play a decelerating role in protein synthesis. Tryptophan is also a precursor of two important metabolic processes: kynurenine synthesis and serotonin synthesis (substance involved in the reaction resulting in the formation of the target substance - an intermediate member of the metabolic pathway).
Accordingly, serotonin is synthesised from the irreplaceable amino acid in the human body - L-tryptophan, while serotonin regulates mood, improves sleep quality and appetite. It is important that serotonin also participates in the regulation of dopamine - if it is lacking, it promotes its release, if there is too much dopamine - it helps to slow down its release. Low serotonin levels are thought to be closely related to depression, anxiety, sleep disorders, weight gain, and other health problems. If there is a deficiency of serotonin in the body, then the person's mood deteriorates, pessimism and apathetic mood increases, as a result of which the desire to do something disappears.
Several laboratories have demonstrated the positive effect of L-tryptophan on sleep quality , as well as the fact that tryptophan reduces the time it takes to fall asleep in patients with mild insomnia or those who take a long time to fall asleep.
Tryptophan has not been found to have any effect on next-day alertness. In patients with moderate to severe insomnia, tryptophan is not as effective as standard sleep aids.
In general, we can say that serotonin regulates the balance of the nervous system; mental stability, mood and also sleep, is the “raw material” for melatonin. In turn, it has been proven that melatonin plays a decisive role in the quality of sleep. Both melatonin and serotonin are formed from the essential amino acid L-tryptophan, which we can only get through food or food supplements.
However, when tryptophan is ingested as part of the diet, it is joined by other large neutral amino acids that compete for the system that transports them all to the brain. As a result, dietary tryptophan intake, unlike tryptophan in the form of food supplements, does not increase tryptophan levels in the brain. Thus, the popular myth that a glass of milk before bed has a calming effect because it contains tryptophan is false.

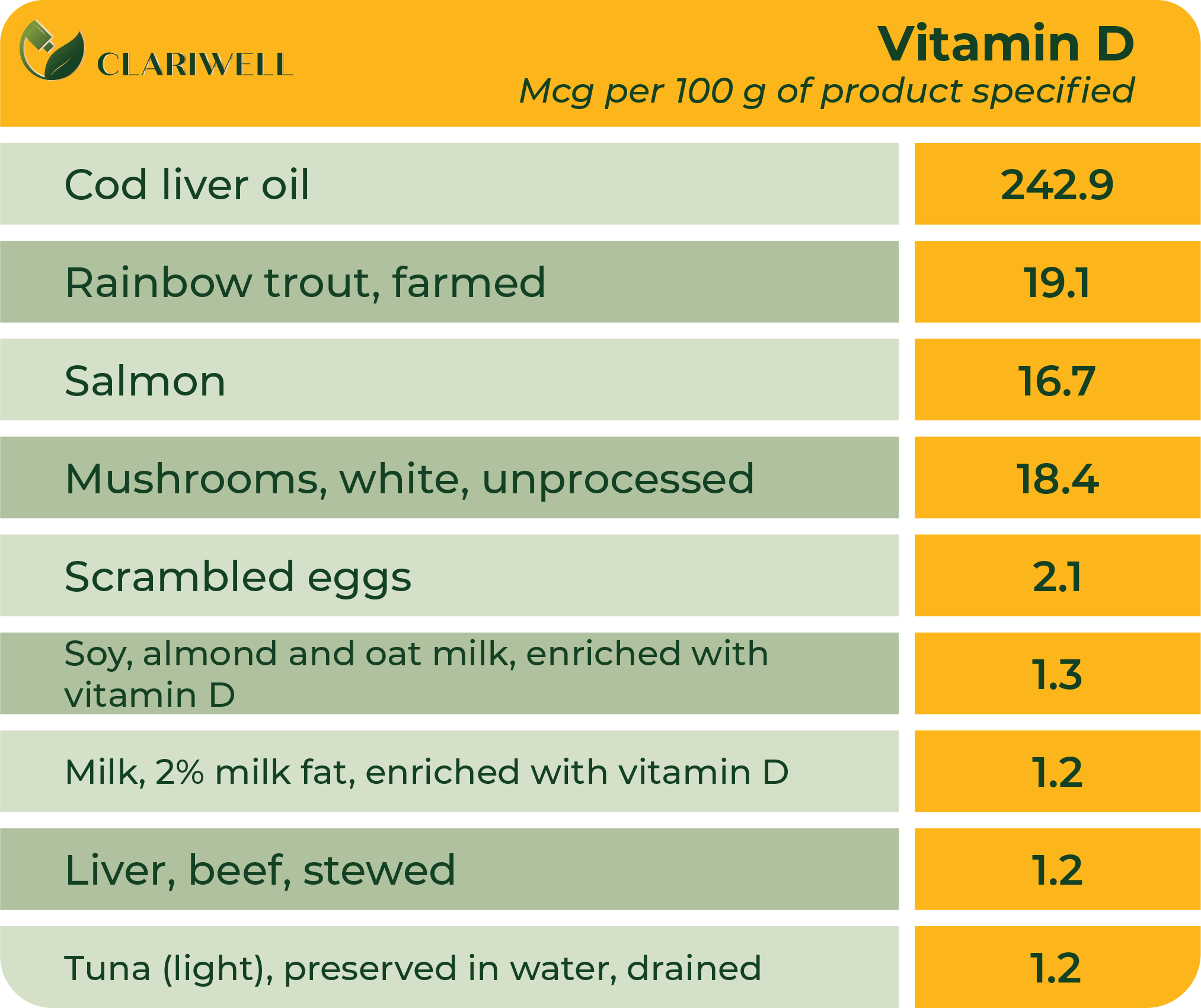
Vitamin D
Vitamin D is a prohormone (hormone precursor) in the group of fat-soluble vitamins. There are five types of vitamin D, ranging from D1 to D5, with two forms being the most common: Vitamin D3 or cholecalciferol and vitamin D2 or ergocalciferol.
Vitamin D helps regulate the amount of calcium and phosphate in the body and is necessary to maintain healthy bones, teeth and muscles. Studies have concluded that vitamin D deficiency is associated with depression and neurocognitive dysfunction, several malignant tumours, and an overall increase in mortality. New studies prove the essential role of vitamin D in maintaining and regulating optimal sleep, as well as the interrelationship between vitamin D concentration, sleep duration and bone metabolism. Vitamin D can modulate innate and adaptive immune responses. Deficiency of vitamin D is associated with increased autoimmunity as well as increased susceptibility to infections.
Vitamin D is a prohormone belonging to the group of fat-soluble vitamins; it is synthesised in the body when the sun's ultraviolet B (UVB) radiation interacts with a precursor molecule, 7-dehydrocholesterol (7-DHC), in the skin (although in healthy people, the internal production of vitamin D is estimated to account for 90% of the total, a small amount of vitamin D is also received from the diet and additional supplements). Vitamin D is then transported in the blood (bound to vitamin D-binding protein) to the liver, where it is hydroxylated to 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25-(OH)D). 25-(OH)D is further converted to the metabolically active form 1α, 25-dihydroxyvitamin D (1α, 25-(OH)2D), mainly in the kidneys.Vitamin D regulates the amount and absorption of calcium ions and phosphates in the small intestine, ensures the formation of bones and teeth, and also helps to strengthen the immune system.
So, for vitamin D to be activated, two metabolic transformations are required - first in the liver - hydrolysis at position 25 (25(OH)D) and then in the kidneys - 1-α-hydrolysis, after which active vitamin D is able to bind to vitamin D receptors to participate in gene transcription and regulated ion (Ca/P) homeostasis.
If we look at the most common forms of vitamin D, D2 (ergocalciferol or calciferol) and D3 (cholecalciferol), it is known that ergocalciferol is mainly obtained from plant sources, formed by UVB radiation in the cell membranes of plants and fungi.
In addition, vitamin D2 is a synthetic molecule that is used to improve food products - added to bread, cereals and dairy products, as well as used in food supplements. Vitamin D3, on the other hand, is obtained from “live” sources, such as fish oil, animal liver and egg yolks. Vitamin D3 is also formed in the skin from provitamin D3 (7-DHC).
Vitamin D deficiency is considered a risk factor for sleep because studies have observed a correlation between vitamin D and sleep duration. Studies of sleep have shown that lower levels of vitamin D are associated with shorter sleep duration in people of all ages. .
An important function of vitamin D is to activate T leukocytes, the cells that actually detect and destroy foreign microorganisms such as viruses. This is why all white blood cells (leukocytes) have vitamin D receptors on their surfaces. Vitamin D can modulate the innate and adaptive immune responses. Deficiency of it is associated with increased autoimmunity as well as increased susceptibility to infections. As immune cells in autoimmune diseases are responsive to vitamin D, it has a beneficial effect in controlling these diseases.
Vitamin D deficiency can occur for various reasons:
- 1. Your eating habits do not include products that are rich in vitamin D; therefore, you do not get enough vitamin D from food;
- 2. Your body does not absorb enough vitamin D from food (malabsorption);
- 3. You spend little time in sunlight or live in a country with little of it, so the body does not receive enough sunlight;
- 4. Your liver or kidneys cannot convert vitamin D into its active form;
- 5. You are taking medicines that prevent your body from converting or absorbing vitamin D.
Vitamin D deficiency can cause a decrease in bone density, which can contribute to osteoporosis and bone fractures. Individuals with vitamin D deficiency have been observed to have improper and restless sleep, as well as other sleep disturbances.
A severe lack of vitamin D can also cause other diseases. It can cause rickets in children. Rickets is a rare disease that causes the bones to become soft and bend. In adults, severe vitamin D deficiency causes osteomalacia. Osteomalacia causes weak bones, bone pain, and muscle weakness.
Researchers are studying vitamin D for its possible connection to several health conditions, including diabetes, high blood pressure, cancer and autoimmune diseases such as multiple sclerosis.
There are some foods that naturally contain vitamin D: fatty fish (such as salmon, tuna, and mackerel), beef liver, cheese, mushrooms, and egg yolks.
Vitamin D can also be obtained from enriched food products. You can check food labels to see if a food contains vitamin D. Food products that are often supplemented with vitamin D include: milk, breakfast cereals and orange juice.
For adults without vitamin D deficiency, the recommended daily dose of vitamin D is 15 mcg or 600 IU, after the age of 70: 20 mcg or 800 IU.
Excessive amounts of vitamin D are toxic. Because vitamin D increases gastrointestinal calcium absorption, vitamin D toxicity results in express hypercalcemia, hypercalciuria, and high serum 25(OH) levels. Hypercalcemia, in turn, can cause nausea, vomiting, muscle weakness, neuropsychiatric disorders, pain, loss of appetite, dehydration, polyuria, excessive thirst, and kidney stones.
In extreme cases, vitamin D toxicity leads to kidney failure, soft tissue calcification throughout the body (including coronary vessels and heart valves), cardiac arrhythmias, and even death.
When taking additional vitamin D, it can interact with several types of medications. Individuals taking these and other medications regularly should discuss vitamin D use and dosage with their healthcare professional.
Orlistat
The weight-loss drug Orlistat (Xenical® and alli®) in combination with a low-fat diet can reduce vitamin D absorption from food and food supplements, thereby reducing 25(OH)D levels.
Statins
Statin drugs reduce cholesterol synthesis. Because endogenous vitamin D is derived from cholesterol, statins can also reduce vitamin D synthesis. In addition, high intakes of vitamin D, especially from food supplements, may reduce the effects of atorvastatin (Lipitor®), lovastatin (Altoprev® and Mevacor®), and simvastatin (FloLipid™ and Zocor®) because these statins and vitamin D compete with each other and the metabolising enzyme itself.
Steroids
Corticosteroid medications are often prescribed to reduce inflammation: budesonide, prednisolone, prednisone, dexamethasone, hydrocortisone, and methylprednisolone (such as Deltasone®, Rayos®, and Sterapred®). These drugs can reduce calcium absorption and interfere with vitamin D metabolism.
Diuretics of the thiazide group
Thiazide diuretics of the thiazide group (such as Hygroton®, Lozol®and Microzide®) reduce urinary calcium excretion. The combination of these diuretics with vitamin D supplements (which increase intestinal calcium absorption) can cause hypercalcemia, especially in the elderly and those with impaired renal function or hyperparathyroidism.
Vitamin D is a prohormone belonging to the group of fat-soluble vitamins. Although vitamin D has traditionally been shown to be involved in calcium homeostasis and bone health, recent studies have found a positive relationship between vitamin D and sleep. In particular, human clinical trials show that low vitamin D levels are associated with poor quality of sleep and short sleep duration. Vitamin D receptors have been found in brain regions involved in sleep regulation, and vitamin D appears to be involved in regulating the sleep-wake cycle.
As we know, vitamin D plays an important role in bone homeostasis and low levels of this vitamin are significantly correlated with low bone mineral density (BMD). Sleep is an important factor in bone metabolism and studies have found a relationship between sleep duration and BMD. In several
self-assessment studies it was reported that decreased sleep duration is associated with decreased BMD and cortical bone thickness.
According to the studies, sleeping less than 5-6 hours is associated with lower BMD and a higher risk of osteoporosis in adults. In children, short sleep duration (<8 h) may be associated with bone mass accumulation disorders during periods of particularly rapid growth. Chronic lack of sleep can directly affect bone metabolism. These discoveries suggest that sleep deprivation may be a risk factor for poorer skeletal health through impaired bone metabolism, may impair bone microarchitecture, and reduce BMD.
In summary, persistent vitamin D deficiency can affect sleep duration, while poor sleep increases the risk of bone fractures and osteoporosis due to impaired bone metabolism.
Vitamin D was used unknowingly to treat infections such as tuberculosis before the advent of effective antibiotics. Tuberculosis patients were sent to sanatoriums where treatment included exposure to sunlight, which was thought to directly kill the tuberculosis. Cod liver oil, a rich source of vitamin D, has also been employed as a treatment for tuberculosis as well as for general increased protection from infections.
The beneficial effects of vitamin D on protective immunity are in part due to its effects on the innate immune system It is known that macrophages recognise lipopolysaccharides (known as endotoxins, which are formed when bacteria are killed) through TLR receptors, which trigger an immune cell response. Engagement of TLRs leads to a cascade of events that produce antimicrobial peptides with potent bactericidal activity that disrupt bacterial cell membranes, such as cathelicidin and beta defensin.
With the direct help of vitamin D, our bodies produce more than 200 antimicrobial peptides, the most potent of which is cathelicidin, a natural broad-spectrum antibiotic. This explains the effectiveness of vitamin D therapy in treating all types of acute respiratory viral infections.
In general, vitamin D helps reduce viral replication by inducing defensins and cathelicidins, and minimises the total amount of cytokines (biochemically active intercommunicating protein molecules produced by immune cells to act on other immune cells) that injure the lung mucosa in inflammatory pneumonia, and helps increase anti-inflammatory cytokines.

California poppy (Eschscholzia californica L.)
California poppies are used medicinally for sleep disorders (insomnia), pain, nervous excitement, as well as in cases of urinary bladder and liver diseases. The California poppy contains a variety of natural compounds, including several alkaloids found only in this plant. Due to its sedative, anti-anxiety and analgesic effects, this plant is used in pharmacy in many countries. The alkaloids found in the California poppy act on GABA (gamma aminobutyric acid) receptors, the main role of which is to reduce the excitability of neurons throughout the nervous system.
California poppies are plants of the Eschscholzia genus of the poppy family (Papaveraceae). Depending on the place of growth, they are divided into two large subspecies E.californica subsp. californica and E. californica subsp. Mexican.
The natural range of the California poppy is the United States (states: California, Oregon, Washington, Nevada, Arizona, New Mexico) and Mexico (States: Sonora and Baja California), but as an ornamental plant it is distributed throughout the world.
The California poppy is an annual (in places where it does not grow naturally) or a perennial 130-152 cm tall plant. The flowers are yellow to orange in colour. It blooms from February to September (in the natural distribution areas) and the flowers have a specific aroma.
Californian poppy leaves are said to have been used by the Indians as a medicine, and the pollen - in cosmetics. The seeds, on the other hand, can be used in cooking.
California poppies are known for their calming, anti-anxiety and sleep-inducing effects. This effect is associated with protopine and allocryptopine. Both alkaloids act as weak stimulants - GABA receptor initiators (agonists) and as acetylcholinesterase inhibitors preventing the breakdown of acetylcholine (ACh) and increasing the duration of action and the level of ACh at the nerve endings, called synapses.[[1:: Atsauces: Fedurco, M., Gregorová, J., Šebrlová, K., Kantorová, J., Peš, O., Baur, R., … Táborská, E. (2015). Modulatory Effects of Eschscholzia californica Alkaloids on Recombinant GABAA Receptors. Biochemistry Research International, 2015, 1–9. doi:10.1155/2015/617620]] Another aporphine alkaloid isolated from this plant, namely N-methyllaurotetanine (NMT), acts as a serotonin 5HT 1A R receptor blocker (antagonist)..Protopine and allocryptopine have been found to block the human serotonin and noradrenaline transporters (hSERT and NERT) and have antidepressant-like effects.
In addition to the mentioned alkaloids, California poppies also contain other active components: alkaloids - cryptopine and chelidonine, as well as flavonoids and glycosides.
California poppies have no narcotic effects and are completely safe to use. It is not an opiate family plant. If the opium poppy has a disorientating effect, the California poppy has a normalising effect on human physiology and psychology. Alkaloids have a calming and relaxing effect on the body and mind, but they work gently.
California poppy is safe for most people when taken correctly perorally for up to three months. There is not enough research on the safety of long-term use of the California poppy.
If surgical intervention is planned: California poppies act on the central nervous system, causing drowsiness and other symptoms. There is a possibility that the California poppy may excessively slow down the central nervous system when used with anaesthesia and/or other drugs used during and after surgery. Stop using California poppy preparations at least 2 weeks before the scheduled surgery.
INTERACTION
Sedative medications (benzodiazepines and CNS depressants)
Interaction assessment: Moderate. Be careful when using this combination. Talk to your health care professional.
California poppies can cause drowsiness. Taking California poppy along with sedative medications can cause excessive drowsiness.
Some of these sedative medications include clonazepam (Klonopin), diazepam (Valium), lorazepam (Ativan), phenobarbital (Donnatal), zolpidem (Ambien), and others.
California poppy is not recommended for:
Insomnia is defined as difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep that is caused by the effects of the day's events and is not related to environmental conditions or insufficient duration of sleep. In the international classification of sleep disorders, insomnia is considered chronic if it persists for a long time - at least three months with a frequency of at least three times a week. In other cases, insomnia is defined as temporary and can be considered corrective, acute, or anxiety-related insomnia.
The Committee on Herbal Medicinal Products (HMPC) and the European Medicines Agency (EMA) have concluded that California poppy can be used to relieve mild symptoms of mental stress and as a sleeping aid.
The sedative and anxiolytic properties of California poppy have been demonstrated in several preclinical studies. With the use of this herb, an increase in sleep time and a decrease in motor activity during sleep were observed.
The chemical composition of California poppy, like all other representatives of the poppy family, is rich in alkaloids, especially protopine, berberine, allocryptopine, escholtzine, and californidine. Flavonoids, especially rutose, have been found in the plant. California poppy contains various carotenoids, such as zeaxanthin, which determine the colour of the plant.
The medicinal properties are related to the alkaloids contained in its chemical composition. Thanks to the alkaloids, California poppy has a calming, antispasmodic and even analgesic effect on the human body.
With the help of California poppy, you can normalise sleep, get rid of insomnia, and the slightly antispasmodic and sedative effect of alkaloids allows the use of the plant extract for the treatment of psychological and physical problems and nervous disorders.

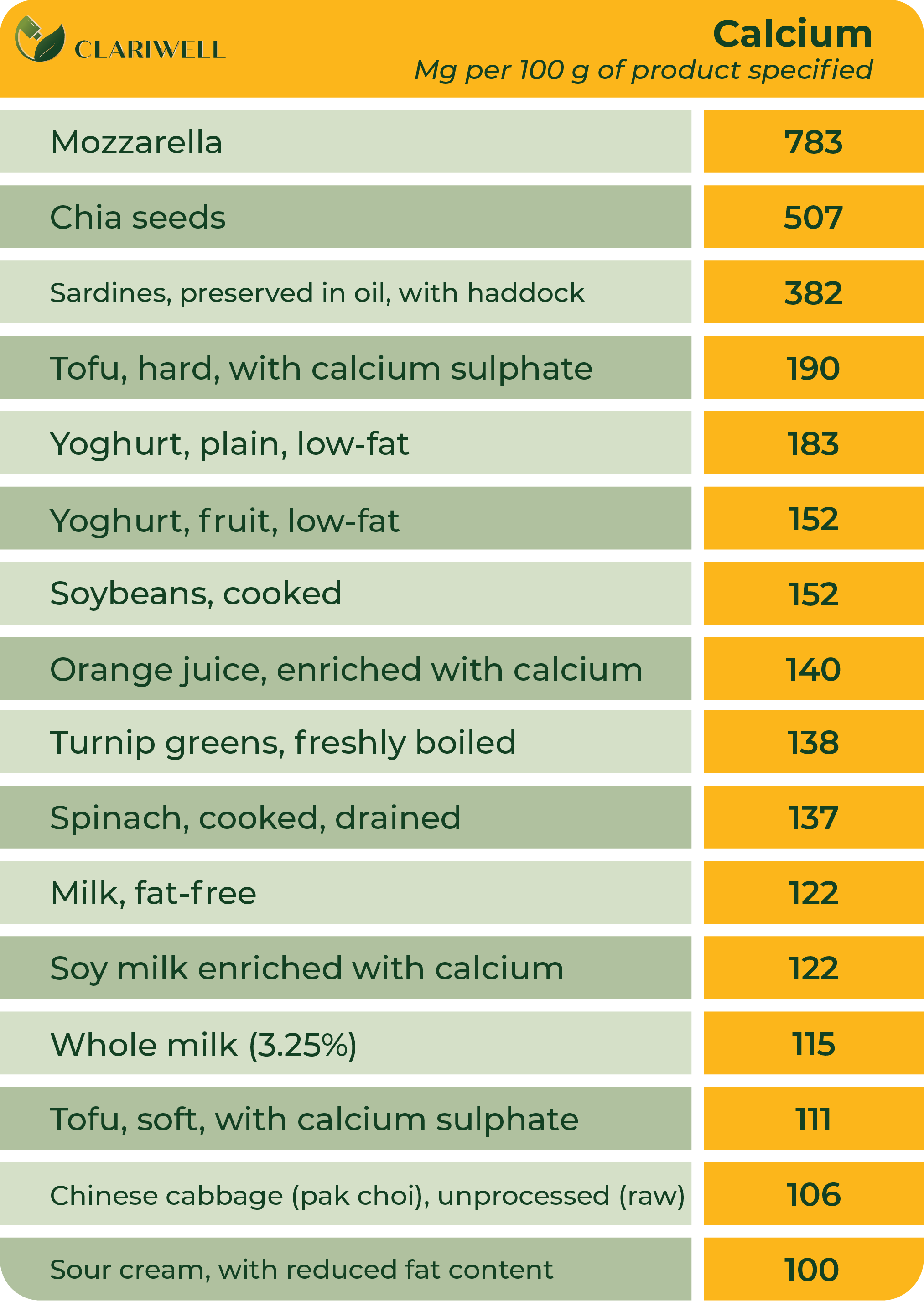
Calcium
Calcium helps build bones and teeth and is essential for nerve, enzyme, heart, muscle and blood clotting functions. Insufficient intake of this mineral can cause bone weakness and increase the risk of fractures in the elderly. Calcium is a natural sleep aid that can help you fall asleep and ensure peaceful sleep because calcium helps the brain use the amino acid tryptophan to produce the natural sleep-inducing hormone melatonin, which helps you fall asleep and stay asleep.
Calcium is the mineral that is mostly associated with healthy bones and teeth, although it also plays an important role in blood clotting, helping muscles to contract. At the same time, calcium regulates a normal heart rhythm and ensures nerve functions, as well as participates in the regulation of hormone activity, reduces neuromuscular excitement, participates in the absorption and use of vitamin B12. About 99% of the calcium in the body is in the bones, with the remaining 1% in the blood, muscles and other tissues.
There are three forms of calcium in the blood plasma: 41% is bound to proteins and in this way it cannot cross the capillary membrane; 9% is in combination with anions and interstitial (tissue) fluid, able to cross the capillary membrane and 50% is ionised and able to cross the capillary membrane. Calcium plays an important role in cellular and extracellular fluid exchange. Calcium ions are necessary in the transmission of nerve impulses.
In neurons, calcium is a key element and it performs multiple tasks. It helps spread electrical signals along axons (nerve cell projections conducting nerve impulses to other nerve cells). It activates synaptic connections to carry neurotransmitters (transmit nerve impulse from synapse to cell) into synapses. Calcium is also involved in memory formation, metabolism and cell growth.
All cells from primitive unicellular organisms to highly differentiated neurons in the cerebral cortex depend on calcium metabolism. This element is important in living organisms, especially in cell physiology, where the movement of Ca2+ in and out of the cytoplasm acts as a signal for many cellular processes.
In food supplements, calcium is found in various forms, where each of the compounds contains a different amount of calcium, or the basic substance, elemental calcium. The following forms of calcium are most commonly used in food supplements:
- • Calcium carbonate (40% elemental calcium)
- • Calcium citrate (21% elemental calcium)
- • Calcium lactate (13% elemental calcium)
- • Calcium gluconate (9% elemental calcium)
Calcium carbonate contains significantly more elemental calcium than other compounds, but requires an acidic food or drink to absorb it. The acid in calcium citrate, on the other hand, promotes the absorption of the compound in an environment of reduced acidity and may be more effective in people taking antacids.
Long-term calcium deficiency can cause changes in teeth (teeth can suddenly become more sensitive, softer and more easily injured; it may be the case that the tooth simply breaks when biting on harder food), cataracts, changes in the brain and osteoporosis, which causes brittle bones.
Symptoms of calcium deficiency:
A person with calcium deficiency may experience:
- • muscle pain, cramps and spasms,
- • pain in the thighs and arms when walking or moving,
- • numbness and tingling in the arms, legs and feet and around the mouth.
These symptoms may come and go, but they do not, however, tend to disappear with activity. More extreme sensations may indicate a more severe deficiency, which can lead to: seizures, arrhythmia, and even death.
Low calcium levels can cause extreme fatigue, which includes a lack of energy and a general feeling of sluggishness. It can also cause insomnia. Fatigue associated with calcium deficiency can also include dizziness and double vision, characterised by a lack of focus, oversight, and confusion.
Prolonged calcium deficiency can cause:
- • dry skin
- • dry, broken or brittle nails
- • brittle hair
- • alopecia, which causes hair loss in the form of spots
- • eczema or skin inflammation that can cause itchy or dry spots
- • psoriasis
Bones store calcium well, but they need high levels of calcium to be strong. If total calcium levels are low, the body can divert some ofthe calcium from the bones to processes needed by the body, making them brittle and prone to fracture.
Over time, too little calcium can cause osteopenia, a decrease in bone mineral density. This can lead to osteoporosis, which makes the bones thinner and more vulnerable to fractures, as well as pain and postural problems.
Some studies suggest that calcium deficiency may be associated with mood disorders, including depression.
Anyone who suspects that calcium deficiency is contributing to depressive symptoms should consult a doctor. After checking your calcium levels, your doctor may recommend additional calcium intake.
For the body to use calcium, it is worth knowing some nuances:
- • together with calcium, vitamin D is needed - both help each other fulfil their functions;
- • in order for calcium to strengthen bones and teeth, sufficient phosphorus must be taken;
- • appropriate enzymes are needed in the gastrointestinal tract, which dissolve the ingested calcium;
- • excessive use of coffee or salt promotes the release of calcium from the body;
- • bone robbers include oxalic acid present in certain vegetables such as rhubarb and spinach;
- • cocoa and black tea negatively affect the absorption of calcium in the body;
- • a large amount of sugar, salt, phosphates and fat in the diet has a negative effect on calcium absorption. Fast snacks, ready-made meals, meat and sausage products contain a particularly large amount of phosphates, so their consumption should be moderate;
- • absorption is hindered by fatty and greasy food, white bread, wheat bran. Absorption can be enhanced by vitamin C and products containing it;
- • any disease of a gastroenterological nature reduces the ability to absorb calcium.
Some foods that are rich in calcium: dairy products such as milk, cheese and yoghurt; beans; figs; broccoli; tofu; soy milk and spinach.
Adults who have not been observed to have a calcium deficiency need 1,000 mg of calcium per day, persons over 51 years of age - 1,200 mg per day.
There is an inverse relationship between calcium intake and absorption. Calcium absorption from food is about 45% when 200 mg/day is taken, but only 15% when intake exceeds 2,000 mg/day. Age can also affect the absorption of calcium taken in from food. Dietary absorption of calcium is as high as 60% in infants and young children, who need significant amounts to build bone, but this drops to about 25% in adulthood and continues to decline with age.
Bloating, gases and constipation may be observed when taking calcium supplements. Very high doses of calcium can cause kidney stones.
Interaction. If you regularly take any prescription or over-the-counter medications, ask your doctor if it is safe to take extra calcium supplements. Calcium can interact with medications for treating heart disease, diabetes, epilepsy, and other diseases. High doses of vitamin D can lead to dangerously high calcium levels. High doses of calcium can also prevent your body from absorbing minerals such as iron and zinc. Try to take calcium one to two hours before or after taking other food supplements or medications. If you happen to take calcium at the same time as other medications or food supplements, they may interact with these products and they will be excreted from your body without being absorbed.
Calcium supplements can interact or interfere with certain medications, and some medications can lower calcium levels in the body. Here are some examples:
Risks. If you have kidney disease, heart problems, sarcoidosis, or bone tumours, do not take calcium supplements unless directed by your doctor.
Overdose. High levels of calcium in the blood can cause nausea, dry mouth, stomach pain, irregular heartbeat, confusion and even death.
Calcium is directly related to our sleep cycles. In one study published in the European Neurology Journal, researchers found that calcium levels in the body are higher during some of the deeper stages of sleep, such as the rapid eye movement (REM) phase. The study concluded that sleep disorders, specifically a lack of REM deep sleep or disturbed REM sleep, are associated with calcium deficiency. Normal sleep patterns were restored after blood calcium levels normalised.
Calcium helps the brain to use the amino acid tryptophan to produce the sleep-inducing substance melatonin.
If the body lacks calcium, nerve impulses may be inhibited and unstable, leading to excessive anxiety or stress. In addition, the nervous system will encounter many obstacles in its operation: the contraction of the heart will be disturbed and the function of muscle reflexes will change. If calcium deficiency is prolonged, insomnia, difficulty falling asleep, poor sleep and frequent awakening will be observed.
Calcium deficiency can cause other related diseases, such as peptic ulcers, which also seriously affect sleep. Lack of calcium stimulates the increase of stomach acid; long-term increased acid will cause damage to the stomach lining, and even ulcers. This process is often accompanied by symptoms such as heartburn, nausea and nighttime stress that causes insomnia.
At the same time, it should be mentioned that there is a close relationship between vitamin D levels and calcium levels, where calcium levels regulate the formation of the deep sleep phase, while the classical functions of vitamin D include intestinal calcium transport and bone mineralisation, which are essential for calcium homeostasis. It is possible that sleep disorders in the case of vitamin D deficiency may be related to altered calcium levels. Lower calcium level in the serum may be associated with more impaired sleep-wake control and rest-activity rhythms. [[2:: Atsauce: Yi-Seon Jeon, Seungyeong Yu, Chaeyeon Kim, Hyuk Joo Lee, In-Young Yoon and Tae Kim1 “Lower Serum Calcium Levels Associated with Disrupted Sleep and Rest–Activity Rhythm in Shift Workers”; Nutrients. 2022 Aug; 14(15): 3021.; Published online 2022 Jul 22. doi: 10.3390/nu14153021]]
 Free delivery to Omniva parcels throughout the Baltics for purchases from 20 euros!
Free delivery to Omniva parcels throughout the Baltics for purchases from 20 euros!